
To create index number series for continuous-time data on prices and quantities of goods exchanged, a theoretical construct called a Divisia index is used. It measures the amount of money in circulation in the economy and is used in official statistics and econometrics. The economist who first proposed and formally analyzed the indexes in 1926 is credited with giving them their name.
The Divisia index is made to take into account changes in quantity and price over time from subcomponents that are measured in different units, like labor hours, equipment investment, and material purchases. As with other index numbers, the resulting series of index numbers has no units and exhibits variations in quantities and/or prices over time.
The Törnqvist index procedure or the Fisher Ideal Index procedures are typically used to create the Divisia index, which is the name given to a series of economic data that follows these procedures. Economic data are typically evaluated based on how well they perform over a period of time rather than in continuous time.
The growth rate of each of the M4 component assets is assigned a weight in the Divisia index for money based on the degree to which they contribute to the provision of transaction services. Since the 1920s, the official data used by the government have been generated using a combination of aggregation theory and index number theory. Induced instability in monetary demand and supply functions was a consequence that was entirely foreseeable and has now materialised.
Statistical index number theory and microeconomic aggregation theory was not as effective. This was the case despite the fact that both theories focus on aggregating data. After they started producing interest, monetary assets stopped being perfect substitutes for one another and became imperfect substitutes. Barnett, who derived the formula for the user cost of demanded monetary services, was the one who came up with the solution to this problem. Because of statistical index-number theory, we are able to precisely track Mt without having to estimate the value of the unknown function. The exact monetary aggregate, Mt, can be tracked exactly in continuous time by the Divisia index, which solves the differential equation. This is possible because Mt is exactly known. The formula has been modified to account for risk aversion and multilateral (international) aggregation while maintaining a common currency zone.
UK banks have monthly data reports are required from financial institutions that have private-sector holdings worth more than one billion pounds.
Since January 2008, data pertaining to UK-resident banks and building societies have been published in accordance with one another. The rate of expansion of Divisia money is calculated by weighting the individual component assets that make up M4 money. The component's usefulness for making transactions, as measured by the user cost of holding that component, is used to determine how much weight it is given in the overall system.
After a change was made to the publication of data for mutually owned monetary financial institutions (MFIs), the Divisia money series became available for use by total monetary financial institutions (MFIs) in December of 2013. The summation index gives the impression that every monetary component contributes exactly the same amount to the overall sum of money, and it considers every component to be a perfect dollar-for-dollar substitute for every other component.
In the final equation, rjt represents the market yield on the jth asset, and rt represents the yield that is available on a benchmark asset that is only held to carry wealth between various time periods.
In contrast to the simple-sum method of monetary aggregation, which simply adds up imperfect substitutes like currency and non-negotiable certificates of deposit, the divisia method divides the total amount of money into smaller pieces. The European Central Bank, the Bank of Japan, and the National Bank of Poland all have access to the Divisia monetary aggregates database for their own internal research purposes.
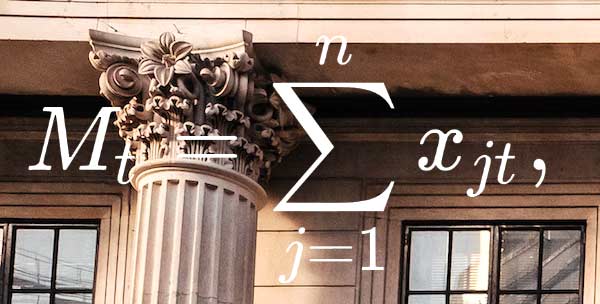
Accounting conventions, as opposed to deep aggregation and index number theory, are the foundation upon which interest rate aggregates are constructed. When non-consolidated components are added together, this results in double counting as well as other violations of established accounting conventions. However, there is still a requirement for the most accurate monetary aggregates, such as m3 and l, to be calculated as appropriately weighted index numbers.
'In our opinion, the simple-sum monetary aggregates provided by the Federal Reserve are completely devoid of any value. They are founded on an obsolete method of economic measurement that has been rendered useless ever since Irving Fishers (1922) published his findings. The Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis is currently providing narrower divisia monetary aggregates, which it refers to as msi (monetary services index).
Calculating and providing narrow-dividend monetary aggregates, such as m1 and m2, is what Cfs does. Our series diverge from those of the St. Louis Fed solely due to the fact that we follow the benchmark-rate procedure established by the Bank of Israel. However, the cfs aggregate is extremely resilient in the face of shifts in the benchmark rate.
On the following dates at 9:00 am Eastern time, Cfs divisia aggregates are scheduled to be made available for public consumption. In 1998, the Federal Reserve stopped publishing its broadest aggregate, which was denoted by the letter 'l.' The data for m3 has been modified to take into account the availability of market data as well as changes in the market's structural makeup.
To convert to the nominal user cost from the real user cost. The interest rate on short-term bank loans is the metric that the Bank of Israel uses to determine the rate of return on pure investment. Shareweights are not overly sensitive to changes in the benchmark rate because the rate appears symmetrically in all terms in the numerator and denominator of the shareweights.
Divisia M4 is a broad aggregate that consists of negotiable money financial assets. Either monetary policy open-market operations or changes in fiscal policy regarding debt financing can cause a shift in the amount of T-bills available for purchase. It might be helpful, from a research standpoint, to disentangle the effects of monetary policy from those of fiscal policy.
The index numbers M3 and l are produced using a competent weighting scheme. We make use of a formula known as the Divisia Monetary Index, which was initially developed and produced by Barnett (1980), who wrote an article entitled Economic Monetary Aggregates: An Application of Aggregation and Index Number Theory. When non-consolidated components are added together, this results in double counting as well as other violations of established accounting conventions.
'In our opinion, the simple-sum monetary aggregates provided by the Federal Reserve are completely devoid of any value. The use of simple-sum aggregates is based on an obsolete method of economic measurement that has been rendered ineffective ever since Irving Fishers (1922) published his work. The Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis is currently providing narrower divisia monetary aggregates, which it refers to as msi (monetary services index).