Best Futures Brokers
The best Futures brokers, must have good regulatory monitoring internationally as well as in Canada. Look for a range of tradable financial instruments, fast withdrawal and deposit options and low fees.
When searching for a Futures broker, there are several key factors to consider for a secure and dependable trading experience. Reputation plays a vital role, so it is recommended to opt for brokers with a proven track record and a positive standing in the industry, as this reflects their reliability. Selecting a Futures broker with the necessary licenses and who is regulated by a reputable financial authority is also crucial. Regulatory oversight ensures investor protection and adherence to industry standards. Additionally, evaluate the range of currency pairs the broker offers, aiming for a diverse selection of major and minor currency futures to maximize trading opportunities. Given the inherent volatility of futures markets, it is essential to be aware of the associated risks. Look for a Futures broker that provides educational resources and risk management tools to support informed decision-making and safeguard invested capital. By carefully assessing these aspects, traders can choose a Futures broker that aligns with their trading objectives and provides a secure and efficient trading environment.
Best Futures Brokers Table of Contents
- Understanding Futures Brokers: A Crucial Component of Trading Futures
- Best Futures Trading Platforms
- What does a futures broker do?
- What Are Futures Brokers, and How Do They Work?
- Can I trade futures in the U.K.?
- Which broker is best for trading futures?
- Do you need a broker to buy futures?
- Is futures trading profitable?
- How to Get Started with a Futures Broker
- Is futures trading risky?
- Future brokers with low intraday margin
- How is the margin calculated for futures trading?
- Embrace the Future of Trading with a Reliable Futures Broker
- Best Futures Brokers List Compared

Understanding Futures Brokers: A Crucial Component of Trading Futures
Futures brokers play a pivotal role in facilitating the trading of futures contracts. These financial professionals act as intermediaries between traders and the futures exchanges, providing essential services and expertise to individuals and institutions seeking exposure to the futures market. In this article, we will explore critical points to understand the significance of futures brokers in futures trading.
Best Futures Trading Platforms
In the ever-evolving world of futures trading, having access to a reliable and feature-rich trading platform is crucial. Suitable futures trading brokers and media can make a significant difference in executing trades efficiently with low trading fees, accessing real-time market data, and implementing trading strategies. Here are some of the best futures trading platforms to consider:
-
IC Markets: Known for its comprehensive trading platform, IC Markets offers a wide range of futures products and competitive pricing. Their platform provides advanced order types, customizable charts, risk management tools, and access to global exchanges. IC Markets also offers a robust API for algorithmic trading.
-
RoboForex: With its robust and intuitive platform, RoboForex caters to novice and experienced futures traders. The platform offers advanced charting capabilities, technical analysis tools, and educational resources. It also provides a paper trading feature for practice and strategy development.
-
XTB: TradeStation is renowned for its professional-grade trading platform, offering many features for futures trading. Traders can use advanced charting, backtesting capabilities, customizable scanning tools, and various technical indicators. XTB also provides access to a wide range of futures markets.
-
AvaTrade: AvaTrade is a popular choice among futures traders, known for its powerful charting and analysis tools. AvaTrade supports discretionary and automated trading, focusing on technical analysis. The platform offers advanced order entry options, backtesting, and strategy development capabilities.
-
CQG: CQG is a robust futures trading platform that provides real-time market data, advanced charting, and order execution capabilities. Traders can customize their trading workspace, access various technical indicators, and utilize advanced order types. CQG offers connectivity to multiple futures exchanges worldwide.
-
ETRADE: ETRADE offers a user-friendly and feature-rich platform for futures trading. It provides real-time streaming quotes, customizable charting tools, and an intuitive order entry system. E*TRADE also provides educational resources and market analysis to assist traders in making informed decisions.
CFDs are complex instruments with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 76-88% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. It would be best if you considered whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
When choosing a futures trading platform, it's essential to consider factors such as reliability, user experience, functionality, and the availability of the specific futures contracts you wish to trade. Additionally, consider the most discount futures broker platform's compatibility with your trading style and the level of support and customer service provided by the platform provider.
Exploring demo versions or trial periods of the best futures broker platforms is recommended to get a feel for their features and interface before committing to a specific forum. Ultimately, the best futures brokers and trading platforms for you will depend on your trading needs, preferences, and level of expertise.
What does a futures broker do?
Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell an underlying asset, such as commodities, currencies, or financial instruments, at a predetermined price and date in the future. A futures broker plays a crucial role in the financial markets, facilitating the trading of futures contracts between buyers and sellers. Here's a closer look at what a futures broker does and their responsibilities:
-
Execution of Trades: One of the primary responsibilities of a futures broker is to execute trades on behalf of their clients. They receive orders from investors or traders and enter them into the futures market. The broker ensures that the transactions are executed accurately and promptly, matching buyers with sellers.
-
Market Access and Connectivity: Futures brokers provide their clients with access to various futures exchanges, such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), or Eurex. They have the necessary technology and infrastructure to connect traders to these exchanges, allowing them to participate in trading futures contracts.
Order Routing and Execution: When a client places an order, the futures broker routes it to the appropriate exchange for execution. Based on the client's trading objectives, the broker may also guide order types, such as market orders, limit orders, or stop orders. They utilize trading platforms or order management systems to transmit orders efficiently and securely.
-
Market Analysis and Research: Futures brokers often provide market analysis and research to their clients. They stay updated on market trends, news, and economic indicators that may impact the prices of the underlying assets. Brokers may offer insights, technical analysis, and recommendations to help clients make informed trading decisions.
-
Risk Management: Futures brokers assist clients in managing their risk exposure. They may advise on position sizing, margin requirements, and risk mitigation strategies. Brokers ensure clients have sufficient funds or margins to cover potential losses or maintain their positions.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Futures brokers must adhere to regulatory requirements and guidelines set by regulatory bodies, such as the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) in the United States. They ensure compliance with reporting obligations, client asset protection rules, and anti-money laundering regulations.
-
Client Support and Education: Futures brokers provide ongoing support and assistance to their clients. They address inquiries, resolve trading-related issues, and offer educational resources to help clients understand futures trading concepts, contract specifications, and trading strategies. Brokers may conduct training sessions or webinars to enhance client knowledge and trading skills.
-
Margin and Account Management: Futures brokers handle their clients' margin requirements and account management. They monitor account balances, margin levels, and collateral requirements to ensure clients meet their obligations. Brokers may provide margin financing options for clients wanting to leverage their positions.
-
Clearing and Settlement: Futures brokers coordinate the clearing and settlement process for trades executed on behalf of their clients. They work with clearinghouses to reconcile trades, ensure proper transfers of funds and assets, and maintain accurate records of transactions.
A futures broker is an intermediary between traders and the futures markets. They execute trades, provide market access and trade value analysis, manage risk, ensure regulatory compliance, offer client support, and handle the administrative aspects of futures trading. By leveraging the expertise and services of a futures broker, traders can navigate the complex world of futures contracts with efficiency and confidence.
What Are Futures Brokers, and How Do They Work?
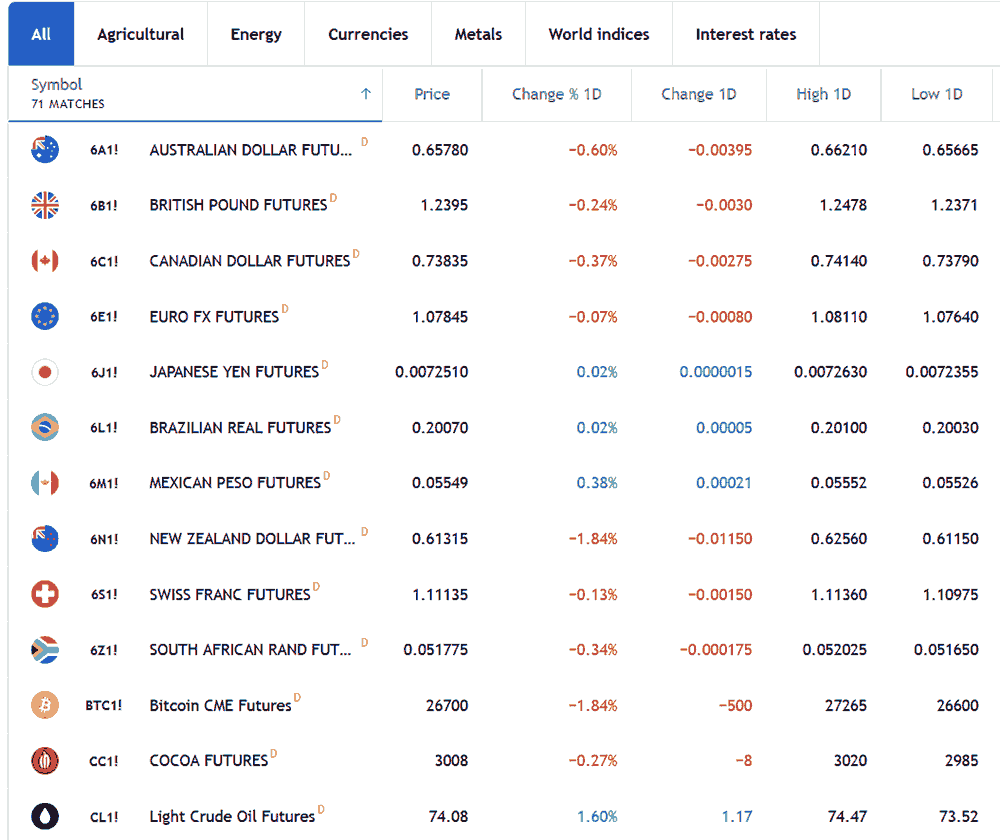
Futures brokers facilitate futures and options trading for individual traders and institutional investors. They act as intermediaries, connecting traders with the futures exchanges where these derivative contracts are traded. Here's a breakdown of what futures brokers are and how they work:
-
Role of Futures Brokers: Futures brokers are licensed professionals or brokerage firms that enable traders to access futures markets. They provide the necessary infrastructure, technology, and expertise to execute futures trades for their clients. Brokers may offer additional services such as market research, educational resources, and risk management tools to assist traders in making informed decisions.
-
Account Setup and Maintenance: Individuals or institutions need to open a futures trading account with a broker to begin trading futures. The account setup process involves submitting required documentation, such as identification and financial information. Once the account is set up, traders can deposit funds into their trading account, which is collateral for their futures trades.
-
Order Execution: Futures brokers offer various trading platforms or software that allow traders to place buy or sell orders for futures contracts. Traders can specify contract specifications, such as the underlying asset, contract size, expiration date, and desired price. The broker's trading platform then sends these orders to the relevant futures exchange for execution.
-
Market Access: Futures brokers provide traders access to various futures markets, including commodities (such as crude oil or gold), stock indices (like the S&P 500), currencies, interest rates, and more. Brokers typically have relationships with multiple exchanges and provide their clients with the ability to trade contracts listed on those exchanges.
-
Risk Management: Futures brokers assist traders in managing the risk associated with futures trading. They may offer risk management tools such as stop-loss orders, which automatically close out positions if the market moves against the trader beyond a specified threshold. Additionally, brokers may provide margin requirements to ensure traders maintain sufficient funds in their accounts to cover potential losses.
-
Clearing and Settlement: Futures brokers handle their clients' clearing and settlement processes. The settlement involves reconciling trades, ensuring that funds and positions are correctly accounted for, and managing the financial aspects of the trade settlement. Brokers also help facilitate the delivery or offsetting of futures contracts before expiration.
-
Client Support: Futures brokers provide customer support to assist traders with account-related inquiries, technical issues, and general trading assistance. They typically offer various communication channels, such as phone, email, or live chat, to address client concerns promptly.
-
Compensation: Futures brokers earn rewards through commissions or fees charged to traders for each executed Trade. These fees vary among brokers and may depend on trade volume, contract type, or the level of service provided. Traders need to understand the fee structure of their chosen broker to manage their trading costs effectively.
It's worth noting that futures brokers must adhere to regulatory requirements and operate within the framework set by financial authorities. This oversight ensures fair trading practices, investor protection, and market integrity.
Overall, futures brokers act as intermediaries between traders and futures exchanges, enabling access to futures markets, executing trades, and providing essential support and services. Their expertise and infrastructure are necessary for individuals and institutions seeking to participate in futures trading.
Can I trade futures in the U.K.?
Yes, you can trade futures in the U.K. Futures trading is a global market, and individuals in the U.K. can participate in futures trading alongside traders worldwide. Here are some key points to consider:
-
Regulatory Framework: In the U.K., futures trading is regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). The FCA oversees financial markets and ensures the fair and transparent operation of futures trading activities.
-
Access to Futures Exchanges: UK-based traders can access various futures exchanges globally, including major exchanges such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), London Metal Exchange (LME), and Eurex Exchange. These exchanges offer various futures contracts, including commodities, stock indices, currencies, and interest rates.
-
Futures Brokerage Accounts: To trade futures in the U.K., you must open a futures brokerage account with a reputable broker. It's essential to choose a broker authorized and regulated by the FCA. The broker will provide the necessary trading platform, market data, and order execution capabilities.
-
Margin Requirements: Like any other country, futures trading in the U.K. involves margin requirements. Traders must maintain certain funds in their trading accounts as collateral to support their futures positions. Margin requirements may vary depending on the specific futures contracts and the broker's policies.
-
Trading Strategies and Risk Management: As a futures trader in the U.K., developing and implementing effective trading strategies is crucial. Risk management may involve conducting market analysis, using technical indicators, and managing risk through tools like stop-loss orders. Familiarize yourself with risk management techniques and stay updated with market trends and news.
-
Tax Implications: It's essential to consider the tax implications of futures trading in the U.K. Consult with a tax advisor or financial professional to understand the tax treatment of your trading activities and any potential obligations.
-
Educational Resources: Various educational resources are available to help U.K. traders learn about futures trading. Online courses, webinars, and educational materials provided by brokers or industry organizations can enhance your knowledge and understanding of futures markets.
Remember, futures trading carries inherent risks, and it's essential to understand the market, trading strategies, and risk management techniques before engaging in futures trading. Consider starting with a demo account or paper trade to gain experience and confidence before trading with real money.
Conduct thorough research, choose a reputable broker, and carefully evaluate your risk tolerance and investment goals before embarking on futures trading in the U.K. or any other country.
Which broker is best for trading futures?
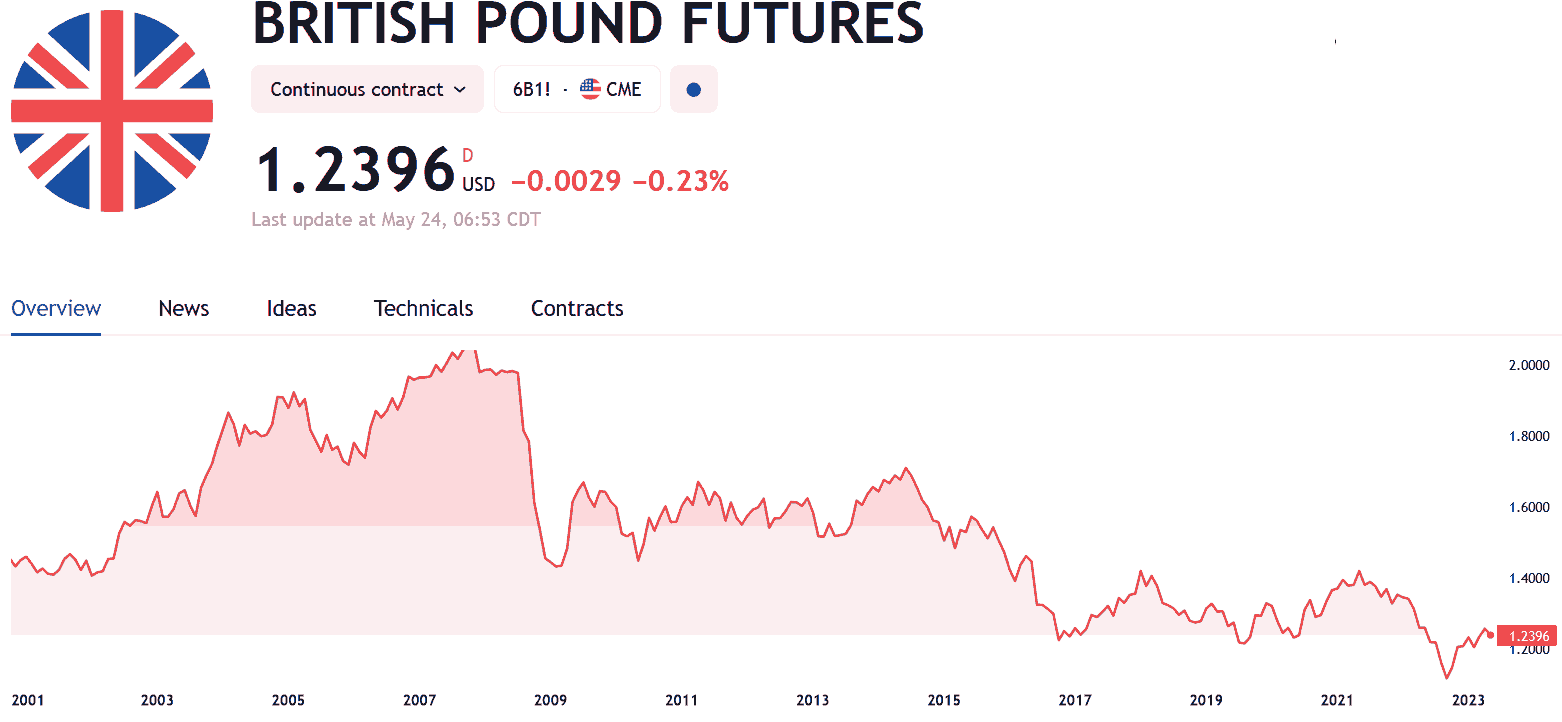
Consider your trading objectives, level of expertise, and the specific futures contracts you wish to trade. Remember to thoroughly research and compare the features, trading platforms, pricing, excellent customer service and support, and regulatory compliance of different brokers. Additionally, ensure that the broker is regulated by a reputable authority, such as the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC).
Opening a demo or paper trading account with a broker is recommended to test their platform and features before committing to real funds. A demo account lets you evaluate the broker's services and determine if they align with your trading style and requirements.
Do you need a broker to buy futures?
You need a broker to buy futures. Brokers serve as intermediaries between traders and the futures exchanges, facilitating the execution of trades on behalf of their clients. Futures trading is conducted through regulated businesses, and individual traders cannot directly access these exchanges. Here's why you need a broker's fee ju buy futures:
-
Access to Futures Exchanges: Futures exchanges, such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) or Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), require participants to be exchange members. Brokers are typically members of these exchanges, which allows them to execute trades on behalf of their clients.
-
Account Setup: To trade futures, you must open a trading account with a brokerage firm. The account setup process involves providing necessary documentation, such as identification and financial information. The broker will verify your information and set up your account, which is a gateway to the futures markets.
-
Order Execution: When you want to buy futures contracts, you place an order through your broker. The broker's trading platform or software allows you to specify the contract, quantity, and price you want to buy. The broker then sends your order to the relevant futures exchange for execution.
-
Risk Management: Brokers provide risk management tools and support to help you navigate the futures markets. They may offer features like stop-loss orders, which automatically close out your position if the market moves against you beyond a specified level. Brokers can also guide you through risk management techniques and help you make informed trading decisions.
-
Account Maintenance and Settlement: Brokers handle various administrative tasks related to your futures trading account. They maintain records of your trades, account balances, and margin requirements. Additionally, brokers take the settlement process, ensuring that funds and positions are correctly accounted for and facilitating the delivery or offsetting of futures contracts.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Brokers are regulated by financial authorities to ensure compliance with rules and regulations, which helps protect investors and maintain market integrity. They must meet certain standards and adhere to specific guidelines, providing traders with confidence and security.
Choosing a reputable and regulated broker that offers the features, trading platforms, and support you require is essential. Consider factors such as contract fees, commission fees, customer service, trading tools, educational resources, and the broker's reputation before selecting a broker for trading futures.
Is futures trading profitable?
Futures trading has the potential to be profitable, but it also carries inherent risks. Whether or not futures trading suits an individual depends on various factors, including trading skills, knowledge of the markets, risk management strategies, and market conditions. Here are some key points to consider:
-
Market Volatility: Futures markets are known for their volatility, which can create opportunities for profitable trades. Volatility allows traders to capitalize on price movements and generate profits. However, it's important to note that volatility can also increase the risk of losses if trades are not adequately managed.
-
Leverage: Futures trading involves margin trading, which means you can control a more significant contract value with a smaller initial investment. This leverage amplifies both potential profits and losses. While power can enhance profitability, it also increases risk, and traders should use it judiciously and manage their positions carefully.
-
Trading Skills and Strategies: Successful futures trading requires a solid understanding of market dynamics, technical analysis, fundamental factors, and trading strategies. Traders must develop a trading plan and employ sound risk management techniques to protect capital and minimize losses. Continuous learning, practice, and refining trading strategies are essential for improving profitability.
-
Risk Management: Effective risk management is crucial in futures trading. Risk management includes setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, managing position sizes based on account size and risk tolerance, diversifying trades, and not overexposing oneself to a single market or contract. Proper risk management helps protect capital and preserve profitability over the long term.
-
Market Knowledge and Research: Staying informed about market trends, economic indicators, and news impacting futures contracts' underlying assets is essential. Conducting thorough research and analysis can help traders identify potential trading opportunities and make informed decisions.
-
Costs and Fees: Traders should consider the costs associated with futures trading, including commissions, exchange fees, and other transaction costs. These costs can impact overall profitability, so it's essential to choose a broker with competitive prices and assess the cost-effectiveness of different trading strategies.
It's crucial to recognize that futures trading involves substantial risk and is unsuitable for everyone. Many traders experience losses, and success in futures trading requires discipline, emotional control, and a long-term perspective. Starting with low fees in a demo or paper trading account is advisable to gain experience and test strategies before committing to natural capital.
Consulting with a financial advisor or seeking guidance from experienced traders, online futures brokers can provide valuable insights and help you make informed decisions regarding the profitability of futures trading. Setting realistic expectations and considering futures trading as a long-term endeavour that requires continuous learning and adaptation to market conditions is also essential.
How to Get Started with a Futures Broker
Starting with a futures broker involves a series of steps to open an account and begin trading futures contracts. Here's a general guide on how to get a minimum account balance and get started with a futures broker:
-
Research and Select a Futures Broker: Conduct thorough research to find a reputable futures broker that suits your trading needs. Consider factors such as commission fees, trading platforms, customer support, educational resources, regulatory compliance, and the range of futures contracts.
-
Complete the account opening process: Visit the broker's website and navigate to the opening section. Follow the instructions to complete the necessary forms and provide the required documentation. Account opening may include personal identification, financial information, and tax-related documents.
-
Fund Your Account: Once your account is approved and set up, you must deposit funds to start trading. Determine the minimum deposit required by the broker and choose a funding method that suits you, such as a bank wire transfer, credit or debit card, or electronic payment system.
-
Familiarize Yourself with the Trading Platform: Most brokers provide a trading platform through which you can access the futures markets. Take the time to familiarize yourself with the platform's features, functionality, and order placement process. Many brokers offer demo accounts that allow you to practice trading without risking real money.
-
Learn About Futures Trading: If you're new to futures trading, educating yourself about the basics is essential. Learn about futures contracts, market terminology, specifications, margin requirements, and trading strategies. Take advantage of your broker's educational resources, including tutorials, webinars, and scholarly articles.
-
Develop a Trading Plan: Before entering the futures market, develop a trading plan that outlines your trading objectives, risk tolerance, and strategies. Define your entry and exit criteria, risk management rules, and profit targets. A well-defined trading plan can guide your decision-making and increase the likelihood of successful trading.
-
Start with Simulated Trading: Consider starting with simulated or paper trading to practice your strategies and gain experience without risking natural capital. Most brokers offer demo accounts with virtual funds allowing you to trade under market conditions. Use this opportunity to refine your trading approach and build confidence.
-
Begin Trading: Once you feel comfortable and confident, you can start trading futures contracts using your live trading account. Monitor the markets, identify trading opportunities, and execute your trades through the broker's platform. Remember to implement proper risk management techniques and adhere to your trading plan.
-
Monitor and Evaluate Your Trades: Continuously monitor your trades, track your performance, and evaluate the effectiveness of your trading strategies. Analyze your successes and failures to identify areas for improvement. Regularly review and adapt your trading plan to align with changing market conditions.
It's important to note that futures trading involves risk, and it's advisable to start with smaller position sizes and gradually increase as you gain experience. Consider seeking advice from experienced traders or consulting with a financial advisor to ensure you make informed decisions about future options.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for educational purposes and should not be construed as financial or investment advice. Trading futures involves substantial risk, and you should carefully consider your financial situation and risk tolerance before trading.
Is futures trading risky?
Futures trading is considered to be risky. It involves the potential for substantial financial losses. Here are some key points to understand about the risks involved in futures trading:
-
Volatility: Futures markets are known for their volatility, which refers to the rapid and significant price fluctuations. Prices can change rapidly in response to various factors such as economic news, geopolitical events, or market sentiment. While volatility can present profit opportunities, it also increases the risk of losses.
-
Leverage: Futures trading involves margin trading, which means you can control a more significant contract value with a smaller initial investment. While leverage can amplify potential profits, it also amplifies losses. Even a tiny adverse price movement can result in significant losses, especially if you have a prominent position or use high leverage.
-
Market Risk: Futures contracts derive their value from underlying assets such as commodities, currencies, or financial instruments. The value of these assets can be influenced by factors such as supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, weather conditions, or economic indicators. Market risk arises from uncertainty and fluctuations in the value of the underlying assets.
-
Counterparty Risk: In futures trading, you enter into a contractual agreement with a counterparty, typically a futures exchange or a brokerage firm. There is a risk that the counterparty may default on their obligations, which can have financial implications for your positions. Choosing a reputable and well-regulated futures broker is essential to mitigate counterparty risk.
-
Liquidity Risk: Liquidity refers to the ability to buy or sell a futures contract without causing significant price movements. Futures markets can experience periods of low liquidity, especially for less actively traded contracts. Limited liquidity can challenge entering or exiting positions at desired prices, potentially resulting in slippage or difficulty executing trades.
-
Systemic Risk: Futures markets are interconnected with other financial needs, and there is a potential for systemic risks that can impact multiple calls simultaneously. Economic downturns, financial crises, or global disruptions can increase market volatility and affect futures trading.
-
Emotional and psychological risks: Successful futures trading requires discipline, dynamic control, and the ability to make rational decisions under pressure. Emotional biases like fear, greed, or overconfidence can negatively impact trading outcomes. Managing emotions and adhering to a well-defined trading plan are crucial to mitigating these psychological risks.
Futures trading involves risks; it may also provide profit opportunities. Well-informed and experienced traders who employ adequate risk management strategies and thoroughly understand the markets can navigate the dangers and succeed. Educating yourself, starting with smaller position sizes, and considering seeking guidance from experienced traders or financial professionals to manage the risks effectively is advisable.
Future brokers with low intraday margin
-
Interactive Brokers: Interactive Brokers is a well-established brokerage known for its competitive margin rates. They offer low intraday margin rates that allow traders to maximize their leverage during the trading day. It's worth noting that margin rates may vary depending on the specific futures contracts.
-
TradeStation: TradeStation is a popular futures broker that caters to active traders. They provide low intraday margin rates, which enable traders to trade larger contract sizes with a smaller account balance. Traders can take advantage of their robust trading platform and competitive commission structure.
-
NinjaTrader: NinjaTrader is a futures trading platform that offers low intraday margin rates. NinjaTrader's low intraday margin allows traders to leverage their positions and potentially increase their trading opportunities. They provide direct access to multiple futures exchanges and offer traders a range of tools and features.
-
AMP Futures: AMP Futures is a futures brokerage that offers low intraday margin rates. AMP Futures caters to individual traders and institutional clients, providing them with the flexibility and low-margin rates they need. They provide access to various futures markets and offer competitive commission structures.
-
Generic Trade: Generic Trade is a futures brokerage known for its low-cost trading solutions. They offer competitive intraday margin rates, allowing traders to maximize their trading capital. Generic Trade provides access to various futures exchanges and offers a user-friendly trading platform.
How is the margin calculated for futures trading?
Calculating the contract specifications: Each futures contract has specific margin requirements set by the exchange. The margin for future trading is calculated based on a concept known as 'initial margin' or 'initial margin requirement'. It is the minimum amount of funds or collateral required to initiate a futures trade. The margin requirements to trade futures contracts may vary based on factors such as the underlying asset, contract size, volatility, and contract liquidity. Margin rates can differ between different futures contracts.
-
Contract Value: The margin requirement is typically a percentage of the total contract value. The contract value is calculated by multiplying the contract size (number of contracts) by the current market price of the futures contract.
-
Leverage: Futures trading involves force, meaning you can control a more significant contract value with a smaller initial investment. The leverage ratio determines the amount of margin required. For example, if the leverage is 10:1, you must deposit 10% of the contract value as a margin.
-
Maintenance Margin: In addition to the initial margin, futures trading also involves a maintenance margin. The maintenance margin is the minimum amount of funds required to keep a futures position open. If the account equity falls below the maintenance margin level, a margin call may be issued, requiring the trader to deposit additional funds to meet the margin requirement.
-
Margin Call and Variation Margin: During the life of a futures position, the contract's market value may fluctuate. As a result, the margin requirement may change. Suppose the market value of the work moves against you. In that case, the exchange or broker may issue a margin call, requiring you to deposit additional funds to restore the margin to the initial level. This process is known as the variation margin. It involves several factors.
Embrace the Future of Trading with a Reliable Futures Broker
Futures brokers play a crucial role in the financial markets by facilitating trading in futures contracts. They are intermediaries between buyers and sellers, ensuring efficient and transparent trading. Through their expertise, technological platforms, and extensive market knowledge, futures brokers provide investors and traders access to a wide range of futures products across various asset classes.
One key advantage of futures brokers is their ability to offer leverage, allowing market participants to control more prominent positions with a smaller initial investment. Leverage can enhance potential returns but also carry significant risks, requiring careful risk management and an understanding of market dynamics.
Furthermore, futures brokers provide valuable research, analysis, and educational resources to help clients make informed trading decisions. They offer real-time market data, technical indicators, and charts that enable traders to monitor price movements, identify trends, and execute timely trades.
The evolution of technology has significantly impacted the futures brokerage industry. Online trading platforms and mobile applications have made it easier for individuals to access futures markets and execute trades. These technological advancements have also improved the speed and efficiency of order execution, reducing latency and enhancing the overall trading experience.
Regulation is critical in ensuring the integrity and stability of futures markets, and reputable futures brokers adhere to strict regulatory requirements. They maintain segregated client accounts, implement risk management protocols, and provide transparent reporting to protect their client's interests.
Futures brokers serve as essential intermediaries, providing individuals and institutional traders with the tools, resources, and access needed to participate in futures markets. Their expertise, technological advancements, and commitment to regulatory compliance make them indispensable partners for those seeking to navigate the complex world of futures trading.
Best Futures Brokers List Compared
| Featured Futures Broker Trading Platform | Account Features | Trading Features |
|---|---|---|
| Used By: 180,000 Instruments Available: 232 Stocks Available: 2100 US Stocks: Yes UK Stocks: Yes German Stocks: Yes Japanese Stocks: Yes Indices: Yes Forex Pairs Available: 61 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: 200 |
Platforms: MT4, MT5, Mirror Trader, ZuluTrade, Web Trader, cTrader, Mac Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: No Losses can exceed depositsVisit |
|
| Used By: 10,000 Instruments Available: 100 Stocks Available: 53 US Stocks: Yes UK Stocks: Yes German Stocks: Yes Japanese Stocks: Yes Indices: Yes Forex Pairs Available: 35 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: 10 USD / 10 EUR |
Platforms: MT4, MT5, Mac, Web Trader, cTrader, Tablet & Mobile apps Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: No Losses can exceed depositsVisit |
|
| Used By: 200,000 Instruments Available: 1000 Stocks Available: 99 US Stocks: Yes UK Stocks: Yes German Stocks: Yes Japanese Stocks: Yes Indices: Yes Forex Pairs Available: 80 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: 100 |
Platforms: Web Trader, MT4, MT5, AvaTradeGo, AvaOptions, Mac, Mobile Apps, ZuluTrade, DupliTrade, MQL5 Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: No 71% of retail CFD accounts lose moneyVisit |
|
| Used By: 10,000 Instruments Available: 100 Stocks Available: 10000 US Stocks: Yes UK Stocks: Yes German Stocks: Yes Japanese Stocks: Yes Indices: Yes Forex Pairs Available: 60 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: 100 |
Platforms: MT4, MT5, IRESS, Mac, Web Trader, Tablet & Mobile apps Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: No Losses can exceed depositsVisit |
|
| Used By: 10,000 Instruments Available: 50 Stocks Available: 0 US Stocks: No UK Stocks: No German Stocks: No Japanese Stocks: No Indices: No Forex Pairs Available: 65 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Minimum Deposit: 10 |
Platforms: MT4, MT5, Tablet & Mobile apps Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: No Losses can exceed depositsVisit |
|
| Used By: 250,000 Instruments Available: 4000 Stocks Available: 1696 US Stocks: Yes UK Stocks: Yes German Stocks: Yes Japanese Stocks: Yes Indices: Yes Forex Pairs Available: 57 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: 0 |
Platforms: MT4, Mirror Trader, Web Trader, Tablet & Mobile apps Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: Yes 76% - 83% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money. Visit |
|
| Used By: 89,000 Instruments Available: 100 Stocks Available: 60 US Stocks: No UK Stocks: No German Stocks: Yes Japanese Stocks: No Indices: Yes Forex Pairs Available: 70 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: 200 |
Platforms: MT4, MT5, Mac, ZuluTrade, Web Trader, cTrader, Tablet & Mobile apps Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: Yes CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. Between 74-89 % of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your moneyVisit |
|
| Used By: 10,000,000 Instruments Available: 1000 Stocks Available: 160 US Stocks: Yes UK Stocks: Yes German Stocks: Yes Japanese Stocks: Yes Indices: Yes Forex Pairs Available: 55 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: 5 |
Platforms: MT4, MT5, Mac, Web Trader, Tablet & Mobile apps Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: Yes CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 77.74% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.Visit |
|
| Used By: 10,000 Instruments Available: 130 Stocks Available: 60 US Stocks: Yes UK Stocks: Yes German Stocks: No Japanese Stocks: No Indices: Yes Forex Pairs Available: 45 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: 100 |
Platforms: MT4, Mac, Mirror Trader, Web Trader, Tablet & Mobile apps Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: No Losses can exceed depositsVisit |
|
| Used By: 142,500 Instruments Available: 200 Stocks Available: 52 US Stocks: Yes UK Stocks: Yes German Stocks: Yes Japanese Stocks: Yes Indices: Yes Forex Pairs Available: 150 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: 100 |
Platforms: MT4, MT5, Web Trader, Tablet & Mobile apps Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: No Your capital is at riskVisit |
|
| Used By: 10,000 Instruments Available: 15000 Stocks Available: 1000 US Stocks: Yes UK Stocks: Yes German Stocks: Yes Japanese Stocks: Yes Indices: Yes Forex Pairs Available: 55 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: 1 |
Platforms: Web Trader, Tablet & Mobile apps Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: No Losses can exceed depositsVisit |
|
| Used By: 10,000 Instruments Available: 148 Stocks Available: 64 US Stocks: Yes UK Stocks: Yes German Stocks: Yes Japanese Stocks: Yes Indices: Yes Forex Pairs Available: 40 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: $100 |
Platforms: MT4, MT5, Mac, Web Trader, Tablet & Mobile apps Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: No Losses can exceed depositsVisit |
|
| Used By: 10,000 Instruments Available: 100 Stocks Available: 1000 US Stocks: Yes UK Stocks: Yes German Stocks: Yes Japanese Stocks: Yes Indices: No Forex Pairs Available: 100 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: 0 |
Platforms: MT4, Mac, ZuluTrade, Web Trader, Tablet & Mobile apps Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: No Losses can exceed depositsVisit |
|
| Used By: 10,000 Instruments Available: 100 Stocks Available: 10 US Stocks: Yes UK Stocks: No German Stocks: No Japanese Stocks: No Indices: Yes Forex Pairs Available: 40 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: 100 |
Platforms: MT4, MT5, Tablet & Mobile apps Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: Yes Losses can exceed depositsVisit |
|
| Used By: 300,000 Instruments Available: 100 Stocks Available: 0 US Stocks: Yes UK Stocks: Yes German Stocks: Yes Japanese Stocks: Yes Indices: Yes Forex Pairs Available: 150 Major Forex Pairs: Yes Minor Forex Pairs: Yes Exotic Forex Pairs: Yes Minimum Deposit: 1000 |
Platforms: MT4, MT5, ZuluTrade, Web Trader, Tablet & Mobile apps Negative Balance Protection: Inactivity Fee: No Losses can exceed depositsVisit |
Best Futures Broker Futures Broker Reviews
Read our details broker Futures Broker Futures Broker reviews, you will find something useful if you are shortlisting a Futures Broker Futures Broker and trading platform.
- IC Markets Review (read our in depth reviews)
- Roboforex Review (read our in depth reviews)
- AvaTrade Review (read our in depth reviews)
- FP Markets Review (read our in depth reviews)
- NordFX Review (read our in depth reviews)
- XTB Review (read our in depth reviews)
- Pepperstone Review (read our in depth reviews)
- XM Review (read our in depth reviews)
- FXPrimus Review (read our in depth reviews)
- easyMarkets Review (read our in depth reviews)
- SpreadEx Review (read our in depth reviews)
- Admiral Markets Review (read our in depth reviews)
- Axi Review (read our in depth reviews)
- HYCM Review (read our in depth reviews)
- Swissquote Review (read our in depth reviews)
Futures Broker Futures Broker Alternatives
Read about and compare Futures Broker Futures Broker alternatives. We have indepth side by side comparisons to help you find Futures Broker Futures Broker related brokers.
- IC Markets Alternatives
- Roboforex Alternatives
- AvaTrade Alternatives
- FP Markets Alternatives
- NordFX Alternatives
- XTB Alternatives
- Pepperstone Alternatives
- XM Alternatives
- FXPrimus Alternatives
- easyMarkets Alternatives
- SpreadEx Alternatives
- Admiral Markets Alternatives
- Axi Alternatives
- HYCM Alternatives
- Swissquote Alternatives
 IC Markets
IC Markets
 Roboforex
Roboforex
 AvaTrade
AvaTrade
 FP Markets
FP Markets
 NordFX
NordFX
 XTB
XTB
 Pepperstone
Pepperstone
 XM
XM
 FXPrimus
FXPrimus
 easyMarkets
easyMarkets
 SpreadEx
SpreadEx
 Admiral Markets
Admiral Markets
 Axi
Axi
 HYCM
HYCM
 Swissquote
Swissquote
